Understanding Markerless Motion Capture with HumanTrak
Available in:
EN
Measuring human movement is central to sound clinical decision-making. Visual estimation alone is often inconsistent, varies between practitioners and fails to reliably detect small but meaningful changes in joint position or control. Markerless motion capture (MOCAP) offers an objective alternative that is fast, repeatable and easy to use in everyday practice.
HumanTrak uses a single depth-sensing camera and machine-learning algorithms to measure patient movement with a high degree of accuracy and minimal setup. This article outlines what defines high-quality movement analysis, how single-camera MOCAP works and how it applies to screening, rehabilitation and performance.
What Defines High-Quality Movement Analysis
High-quality movement analysis requires a measurement that is objective, consistent and sensitive enough to detect changes over time. In clinical practice, decisions often hinge on subtle improvements, such as a few degrees of knee valgus, a small increase in hip flexion or a measurable change in trunk rotation. These differences are almost impossible to track visually, making objective tools essential.
…[subtle improvements] are almost impossible to track visually, making objective tools essential.
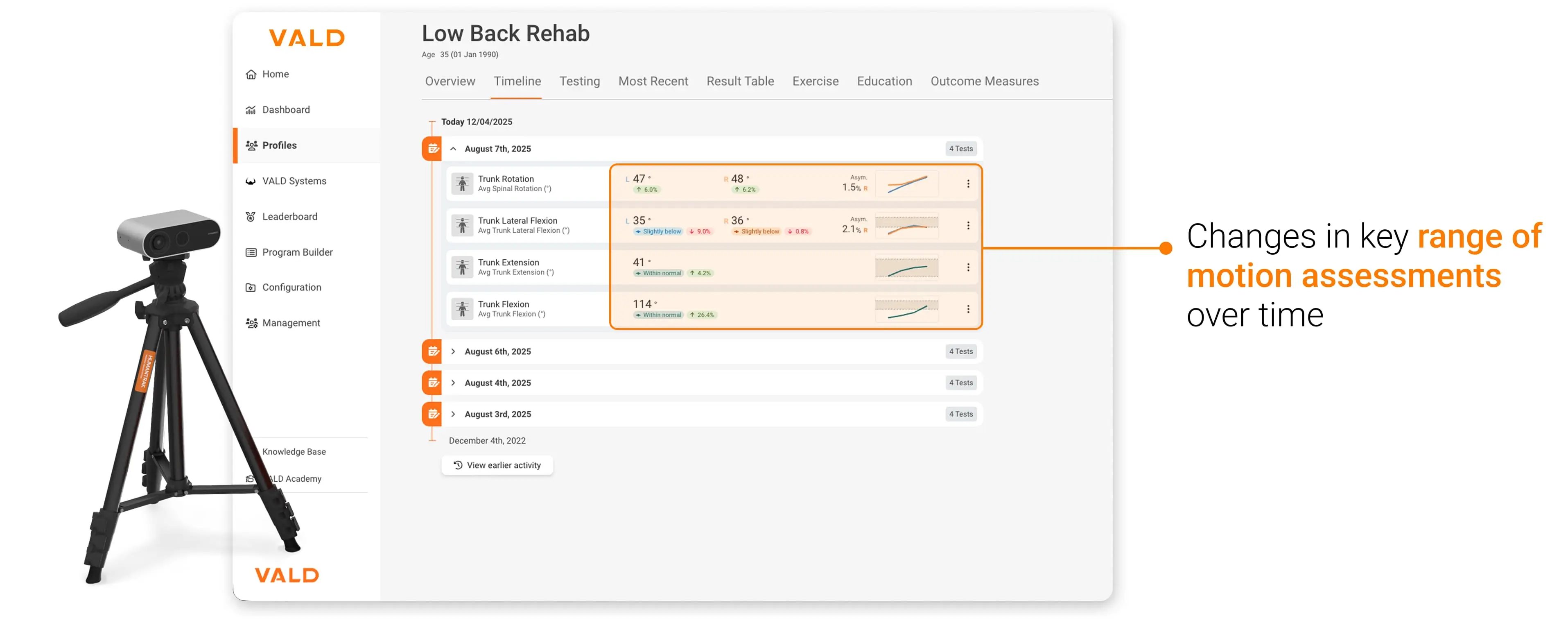
HumanTrak can detect small improvements in motion, as visualized in the timeline view in VALD Hub.
A robust movement analysis system must produce reliable results when a patient is retested under similar conditions, regardless of who conducts the assessment. Standardized testing procedures (consistent cues, camera distance and positioning) help minimize practitioner-driven variation and ensure that changes in movement reflect true progress.
Accurate identification of joint positions and angles is equally important. Small errors can produce misleading interpretations. Markerless MOCAP technologies, such as HumanTrak, eliminate the inconsistency of manual landmarking and automate the detection of anatomical points, improving measurement repeatability.
To truly guide decision-making, movement analysis must also offer whole-body insight. A knee angle alone cannot explain a lunge strategy; the pelvis, trunk and foot all contribute. High-quality movement data accounts for these interactions and more, revealing movement trends and strategies that even a well-trained eye cannot see.
How Single-Camera Markerless MOCAP Works
Modern markerless MOCAP uses depth-sensing technology and machine learning to turn raw footage into actionable movement data. HumanTrak uses an RGB-D camera to capture both color and depth, enabling highly accurate reconstruction of body position.
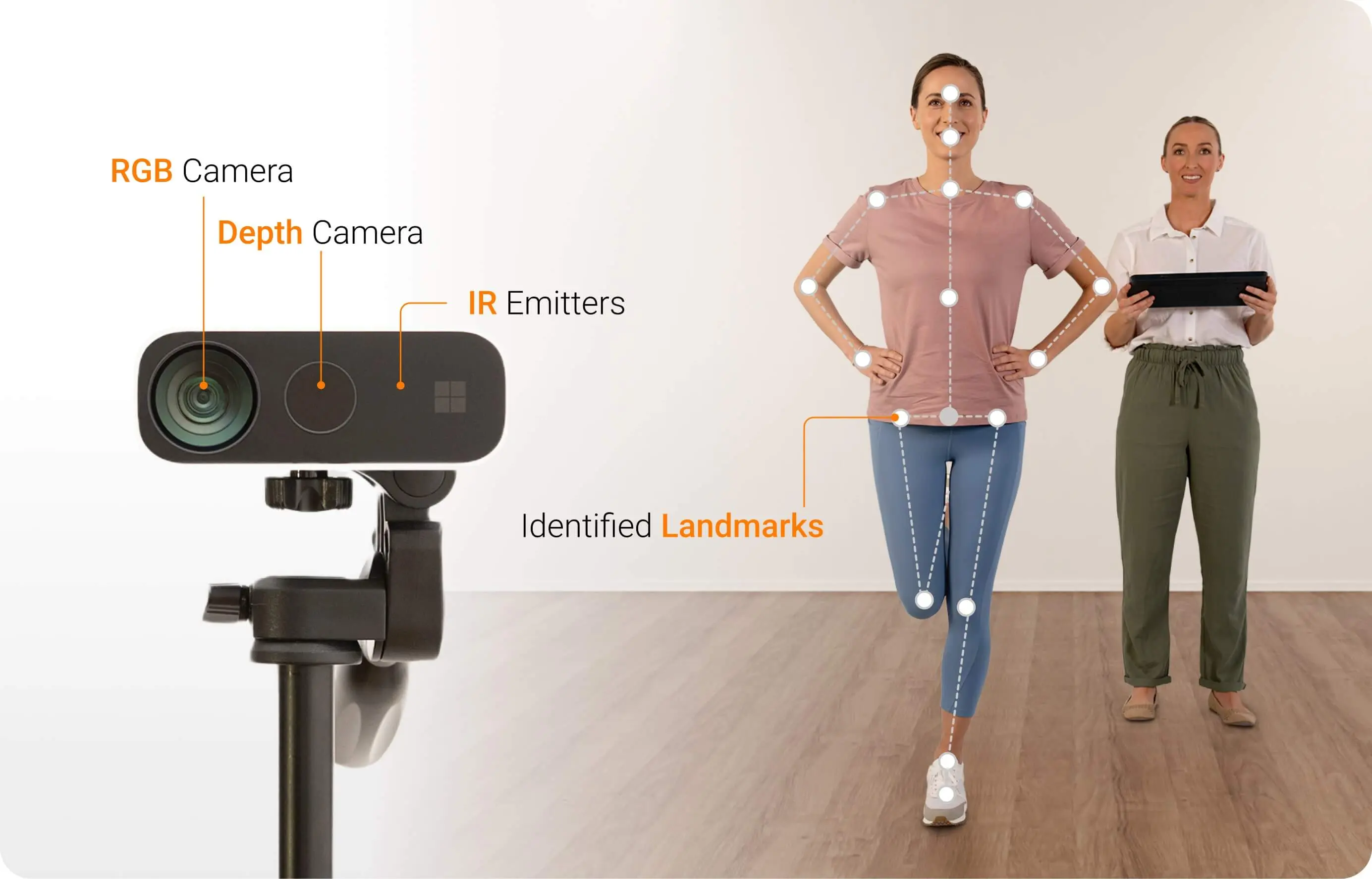
HumanTrak uses an RGB-D camera to capture both color and depth, enabling highly accurate reconstruction of body position.
The workflow begins with the camera capturing a movement. The camera’s depth-sensing technology uses near-infrared light to determine the distance between the camera and the user. A trained machine-learning model identifies the patient, locates anatomical landmarks and reconstructs a 3D skeleton. This reconstruction allows HumanTrak to track joint translations (how far a joint shifts) and rotations (how far it turns) in all three anatomical planes.
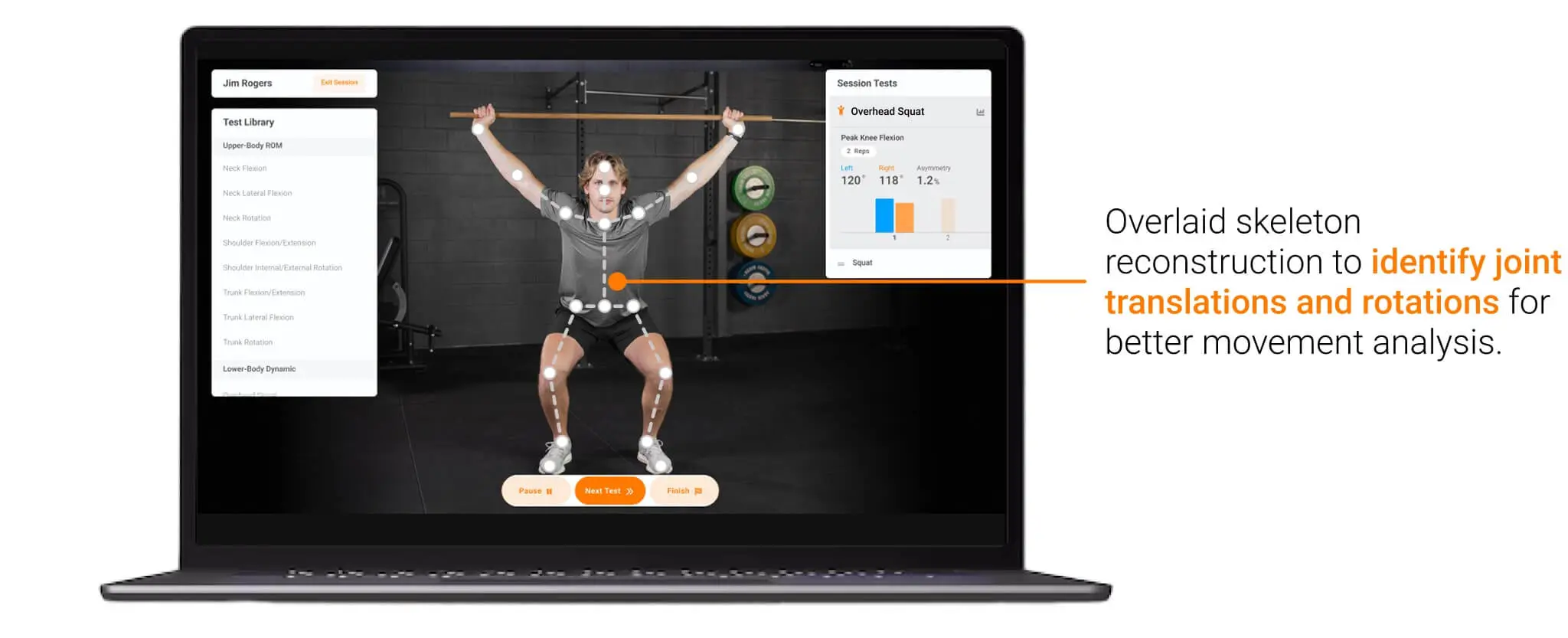
Overlaid skeleton reconstruction to identify joint translations and rotations for better movement analysis.
From this model, HumanTrak calculates how joints translate and rotate during movement. Repetitions and key movement phases are automatically identified, allowing metrics such as peak joint angles, ranges of motion and displacements to be computed and displayed in clear visual reports.
HumanTrak’s MOCAP pipeline progresses through the following:
- RGB-D Sensing: Capturing synchronized color and depth data
- ML-Based Joint Detection: Identifying body joints from sensor data
- 3D Skeleton Reconstruction: Modeling full-body posture and motion
- Joint Kinematics Calculation: Computing translations and rotations over time
- Automated Repetition Detection: Segmenting movement into meaningful phases
- Metric Generation and Reporting: Translating kinematics into interpretable outputs
How HumanTrak Describes Movement
HumanTrak’s reporting framework uses joint translations, joint rotations and anatomical planes to provide a consistent language for describing human movement.
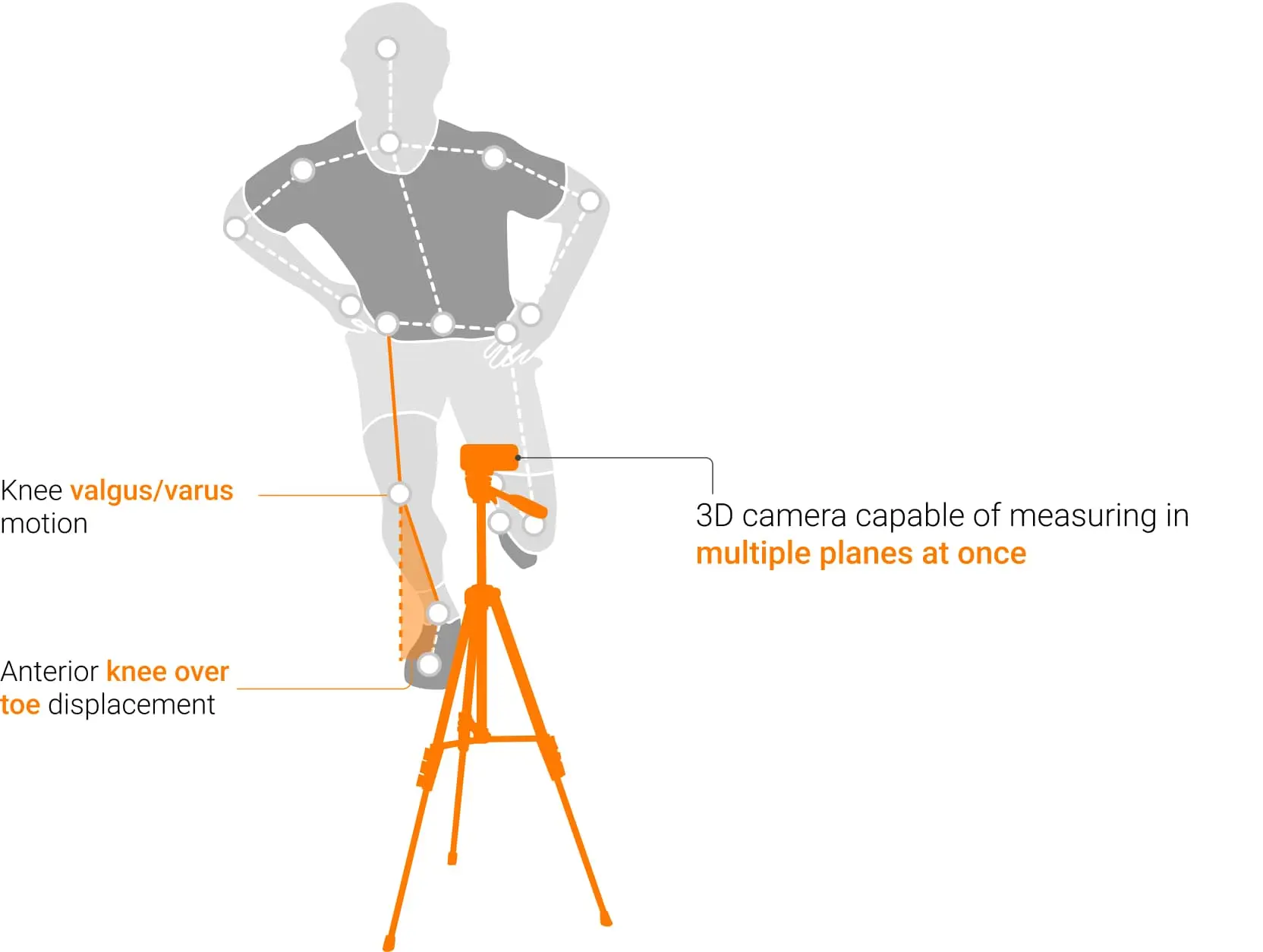
Translations quantify how joints shift in three-dimensional space. This could be lateral knee movement during a squat or pelvic drift during gait. Rotations describe angular motion, such as trunk rotation during a turn or hip internal rotation in a lunge. By combining both, HumanTrak can highlight not only obvious deviations but also subtle control issues that influence movement quality.
By combining [translation and rotation], HumanTrak can highlight not only obvious deviations but also subtle control issues that influence movement quality.
Patient performing a single-leg squat with HumanTrak tracking multiple measures at once.
Anatomical planes provide an organized way to contextualize motion: flexion and extension in the sagittal plane, side-to-side motion in the frontal plane and rotation in the transverse plane. Movement rarely occurs in a single plane, so understanding these interactions is crucial for accurate interpretation.
HumanTrak also estimates the location of the center of mass (CoM) by combining segment positions with population-based mass distribution data. CoM reflects whole-body stability – how effectively a patient maintains their balance relative to their base of support. Watching how CoM shifts during tasks like single-leg balance or tandem stand provides insight into control strategies and compensations that are invisible to the naked eye.
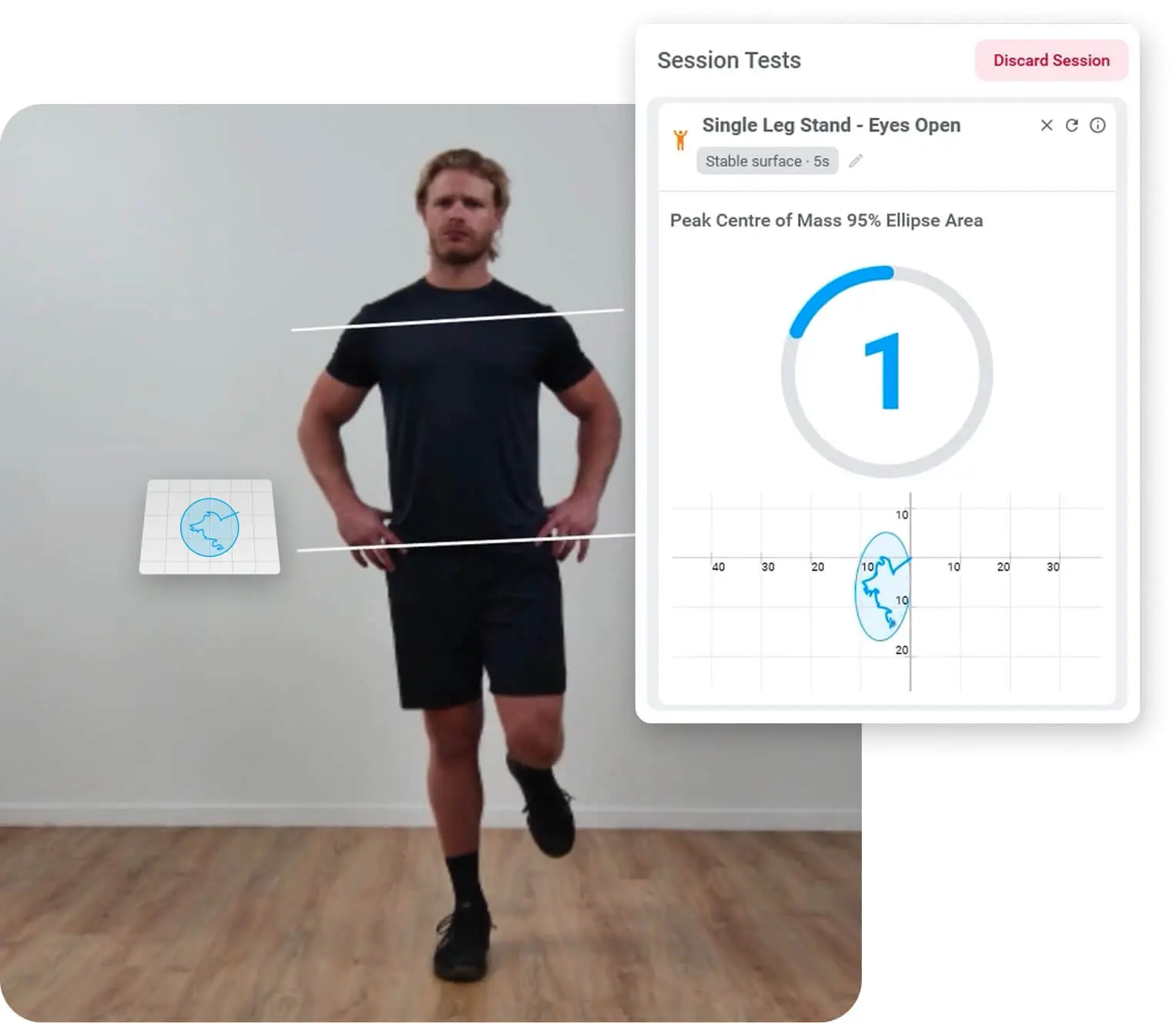
Balance assessment with HumanTrak measuring a top-down view of CoM displacement.
Why Markerless MOCAP Is Becoming a Clinical and Performance Standard
Traditional multi-camera MOCAP systems produce excellent data but require extensive setup, controlled environments, markers or suits and often specialist staff. For most clinics, gyms and field environments, this level of complexity is impractical.
Markerless MOCAP overcomes many traditional limitations by removing the need for physical markers and automating movement analysis. Some systems operate with a single camera for rapid setup and minimal space requirements, while others use multiple cameras to enhance tracking accuracy.
Although multi-camera MOCAP systems may seem enticing, assessments require detailed calibration before every use and skilled operators to perform testing procedures. Conversely, single-camera systems, such as HumanTrak, are “plug and play,” lowering the barrier to entry and providing fast, reliable assessments for busy practitioners.
Assessments with systems like HumanTrak can be repeated frequently due to their ease and speed of use – an important advantage when monitoring rehabilitation progress or tracking training effects.
Assessments with systems like HumanTrak can be repeated frequently…an important advantage when monitoring rehabilitation progress or tracking training effects.
Practitioners are adopting markerless MOCAP not only for its practicality but for its consistency. Automated landmark detection removes the variability introduced by manual marker placement. Reports are generated instantly, reducing administrative burden and supporting real-time discussions with patients or athletes.
Key reasons practitioners value markerless MOCAP:

These advantages position markerless MOCAP as the emerging standard for objective movement assessment in real-world environments.
Applying MOCAP Across Screening, Rehabilitation and Performance
MOCAP becomes most valuable when used consistently across the continuum of care – from early identification of movement limitations to monitoring rehabilitation and guiding performance training.
MOCAP becomes most valuable when used consistently across the continuum of care…
During screening, MOCAP data helps identify asymmetries or restrictions that may increase injury risk. Establishing objective baselines also allows groups such as sports teams, workplaces or patient cohorts to track changes over months or seasons. This clarity helps direct preventative programs before issues arise, while VALD Norms provides population-level reference points that help contextualize patient results and identify whether values fall within expected ranges for similar groups.

In rehabilitation, session-to-session comparisons indicate whether a patient is improving in mobility, control or movement quality. Objective benchmarks can validate clinical decisions such as progressing the load, advancing exercise difficulty or clearing patients for higher-intensity tasks. Clear, visual reports also support communication by showing patients exactly how their movement is changing.
In performance settings, MOCAP highlights the strategies an athlete uses to generate and absorb force. Two athletes may perform a jump, lunge or squat to the same standard but rely on different strategies to achieve it. Understanding these strategies helps refine techniques, reduce compensations and tailor training programs with greater precision. Tracking these patterns across a season provides insight into adaptation, fatigue or readiness.
Practical Takeaways
Markerless MOCAP provides practitioners with an accessible, objective and scalable approach to understanding movement. HumanTrak combines depth sensing and machine learning to capture full-body motion with ease, supporting more confident decision-making across screening, rehabilitation and performance.
By integrating MOCAP into routine practice, practitioners gain clearer insights into how patients move, how they improve and how their strategies evolve over time…
By integrating MOCAP into routine practice, practitioners gain clearer insights into how patients move, how they improve and how their strategies evolve over time – ultimately improving outcomes for patients and athletes alike.
If you would like to learn more about how HumanTrak can enhance movement assessment in your practice, please get in touch.
